Types of Solutions
Anystates of matter(solid, liquid, or gas) can participate as a solute and as a solvent during the formation of a chemical solution. Therefore, depending on the physical states of solute and solvent, the chemical solution may be classified into the following different types.
|
Types of solution |
Solute |
Solvent |
Examples |
|
Gas-gas |
gas |
gas |
A mixture of gases that do not undergo chemical reactions. For example, a mixture of air,hydrogen, andhelium. |
|
Gas-liquid |
gas |
liquid |
An aqueous hydrogen chloride, aqueous carbon dioxide, aqueous ammonia, etc. |
|
Gas-solid |
gas |
solid |
Hydrogen is absorbed by platinum or palladium to form a gas-solid solution. |
|
Liquid-gas |
liquid |
gas |
Aerosol or water vapour in the air. |
|
Liquid-liquid |
liquid |
liquid |
A mixture of water and ethanol or a mixture ofbenzeneand toluene. |
|
Liquid-solid |
liquid |
solid |
Combination of sodium and mercury in sodium-amalgam (Na/Hg) or a combination of sodium andzincin zinc-amalgam (Zn/Hg) |
|
Solid-liquid |
solid |
liquid |
The aqueous sodium chloride, sugar, etc. |
|
Solid-solid |
solid |
solid |
Alloys like brass (a mixture ofcopperand zinc) or bronze (a mixture of copper andtin). |
|
Solid |
solid |
gas |
Camphor in nitrogen gas |
· Aqueous solution:An aqueous solution is created by the dissolution of a solute in water. Examples of aqueous solutions include water-based solutions of glucose, sodium chloride, and soap.
· Non-Aqueous solution:When a solute is dissolved in a liquid that is not water, such as benzene,acetone, ethanol, carbon disulfide, and so on, the result is a non-aqueous solution.
Based on the quantity of solvent added:
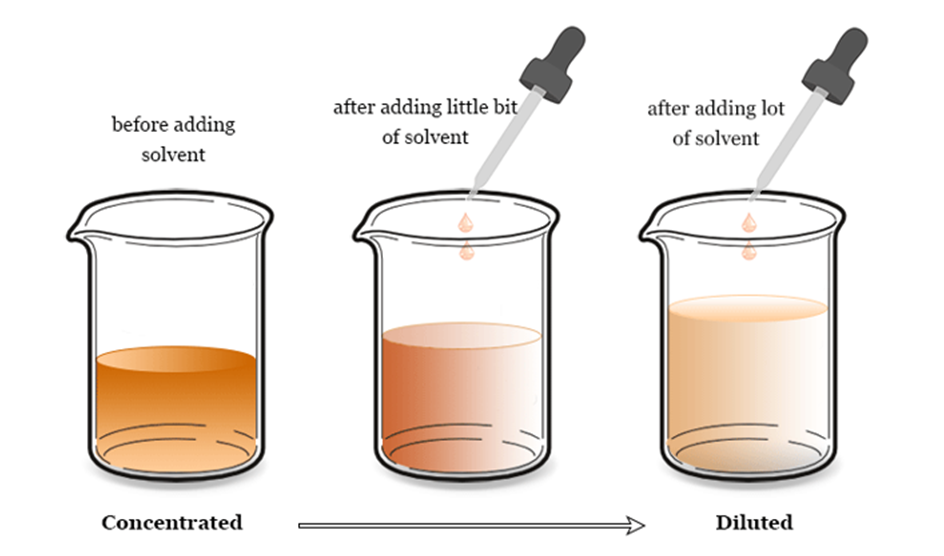
· Concentrated solution:In a concentrated solution, there is a significant amount of the solute in the provided solvent. Examples include black tea, apple juice, and brine solution.
· Dilute solution:A diluted solution contains a greater proportion of solvent.
· Saturated solution:In a saturated solution, the solute is entirely dissolved in the solvent at the specified temperature.
· Unsaturated solution:A solution that allows for more solute dissolution at the same temperature is said to be unsaturated.
Supersaturated solution:When a solute starts to precipitate out after being dissolved at a specific concentration and temperature, the solution is said to be supersaturated.