Protozoa
- Protozoa or Cornelius protozoans (from Greek proton "first" and zoa "animals"; singular protozoon; (the word "protozoan" is originally an adjective, used as a noun) are microorganisms classified as unicellular eukaryotes.
- All Protozoans are heterotrophs and live as predators orparasites.
- They are believed to be primitive relatives of animals.
- They may be broken down into four primary categories, which are as follows:
- Ciliated Protozoans:
- They are mostly Aquatic animals.
- They are actively moving organisms because of the presence of thousands of cilia.
- They have a cavity (gullet) that opens to the outside of the cell surface.
- The coordinated movement of rows of cilia causes the water laden with food to be steered into the gullet. Example- Paramecium.
- Ciliated Protozoans:
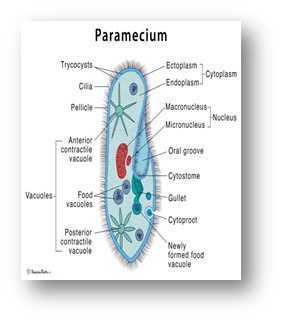
- Amoeboid protozoans:
- They may be found in saltwater, as well as freshwater, and wet soil.
- They have pseudopodia (false feet) which help to change their shape and to capture engulf food. E.g. Amoeba.
- Marine forms have silica shells on their surface.
- Some of them such as Entamoeba are parasites.
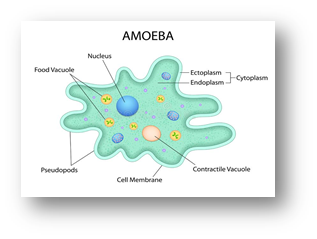
- Flagellated protozoans:
- As the name suggests, the members of this group have flagella.
- They can be free-living as well as parasitic.
- Trypanosoma species can spread some dangerous diseases such as sleeping sickness.
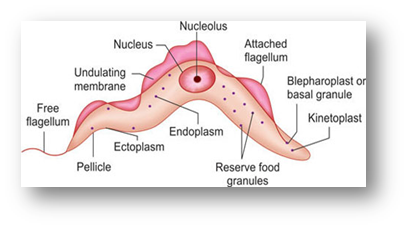
Trypanosoma
- Sporozoans:
- This includes diverse organisms that have an infectious spore-like stage in their life cycle.
- The most notorious is Plasmodium (malarial parasite) which causes malaria which has a staggering effect on human population.

Plasmodium