Chloroplast
- Most of the chloroplasts in green plants are found in the mesophyll cells of the leaves.
- They can have various shapes, including lens-shaped, oval, spherical, discoid, or ribbon-like, with variable length and width (typically 5-10µm in length and 2-4µm in width).
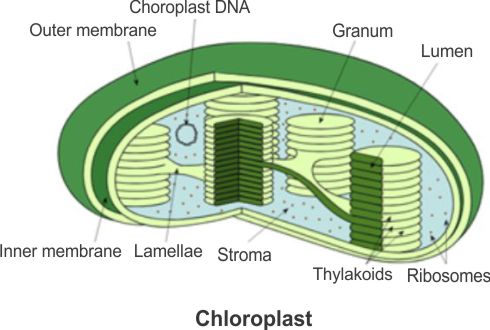
- Like mitochondria, chloroplasts are also double-membrane-bound organelles.
- The inner membrane is relatively less permeable.
- The space enclosed by the inner membrane is known as the stroma.
Thylakoids and Grana:
- Chloroplasts contain organized, flattened membranous sacs called thylakoids, which are present in the stroma.
- Thylakoids are arranged in stacks like piles of coins, known as grana (singular: granum), and the membranes connecting thylakoids are called stroma lamellae.
- Thylakoids enclose a space known as a lumen.
- The stroma of the chloroplast contains enzymes necessary for the synthesis of carbohydrates and proteins.
Genetic Material:
- Chloroplasts contain small, double-stranded circular DNA molecules and ribosomes.
- Notably, the ribosomes in chloroplasts are smaller (70S) than the cytoplasmic ribosomes (80S).