Lipids: Versatile Biomolecules
Lipid Definition:
- Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic (water-insoluble) organic molecules. They are not true polymers like proteins and carbohydrates.
Types of Lipids:
-
Fats:
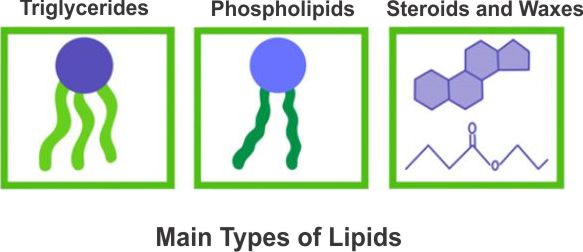
- Structure: Fats are composed of glycerol and three fatty acid molecules.
- Function: Energy storage, insulation, cushioning.
-
Oils:
- Structure: Oils are similar to fats but are liquid at room temperature.
- Function: Energy storage, especially in plants.
-
Phospholipids:
- Structure: Phospholipids consist of glycerol, two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a polar head group.
- Function: Major component of cell membranes, forming a phospholipid bilayer.
-
Steroids:
- Structure: Steroids have a characteristic four-ring structure.
- Function: Precursors for hormones (e.g., estrogen, testosterone) and important in membrane structure (e.g., cholesterol).
Key Characteristics of Lipids:
-
Hydrophobic Nature:
- Lipids are nonpolar and do not mix well with water. This property is important for their functions.
-
Energy Storage:
- Lipids store a high amount of energy per gram, making them efficient energy storage molecules. They provide a significant source of ATP when oxidized.
-
Insulation and Protection:
- Adipose tissues, composed of fat cells, serve as insulation against heat loss and provide cushioning around organs, protecting them from physical damage.
-
Structural Role:
- Lipids are vital components of cell membranes, contributing to their flexibility and integrity. Phospholipids form the lipid bilayer in cellular membranes.