HYDROGEN PEROXIDE
Preparation of hydrogen peroxide
(a) Na2O2+ dil. H2SO4  H2O2+ Na2SO4
H2O2+ Na2SO4
(b) BaO2+ H2SO4  H2O2+ BaSO4↓
H2O2+ BaSO4↓
(c) 3BaO2+ 2H3PO4  3H2O2+ Ba3(PO4)2↓
3H2O2+ Ba3(PO4)2↓
(d) BaO2+ H2O + CO2 H2O2+ BaCO3
H2O2+ BaCO3
(ii) By electrolysis of Ammonium hydrogen sulphate (NH4HSO4) in presence of excess of H2SO4
(a) NH4HSO4→ NH4SO-4+ H+
at anode
2NH4SO-4 → (NH4)2S2O8+ 2e−
Ammonium perdisulphate
at cathode:−
2H+ + 2e− → H2↑
On heating Ammonium perdisulphate in presence of water hydrolysis occurs and H2O2 is produced.
(NH4)2S2O8+ 2H2O 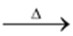 H2O2+ NH4HSO4
H2O2+ NH4HSO4
(iii) Auto oxidation of 2−ethyl or Butyl Anthraquinone
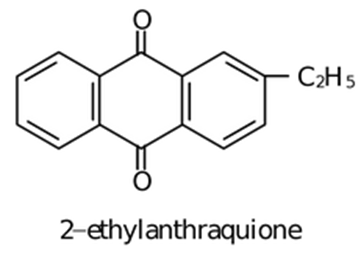
![]()
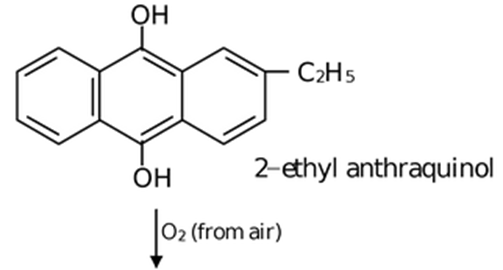
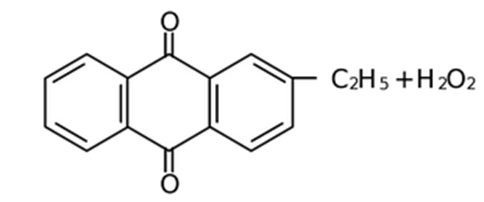
The aqueous product contains 20% H2O2.
Physical Properties of hydrogen peroxide
(1) Pale blue colour, diamagnetic, surupy liquid.
(2) Unstable in presence of sunlight.
(3) Have high dielectric constant and therefore its aqueous solution is very good solvent for ionic compounds.
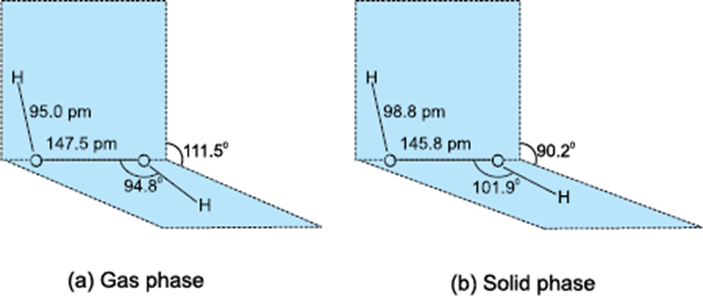
Structure of hydrogen peroxide
1. The structure of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) consists of two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms bonded together.
2. The molecule has a non-planar shape.
Chemical Properties of hydrogen peroxide
It acts as an oxidising as well as reducing agent in both acidic and alkaline media. Simple reactions are described below.
(i) Oxidising action in acidic medium
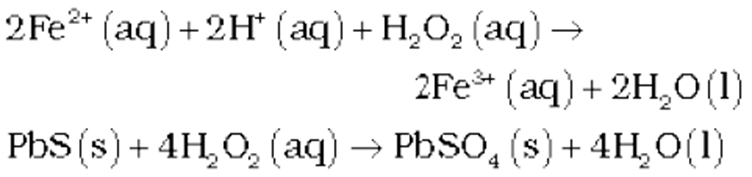
(ii) Reducing action in acidic medium
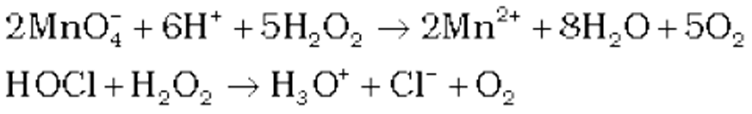
(iii) Oxidising action in basic medium
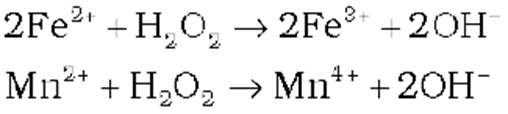
(iv) Reducing action in basic medium
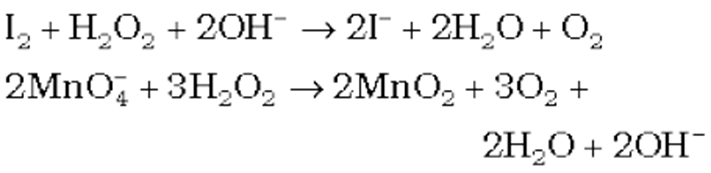
Storage of hydrogen peroxide
H2O2decomposes slowly on exposure to light.
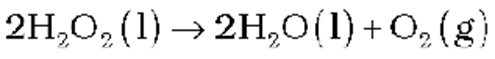
In the presence of metal surfaces or traces of alkali (present in glass containers), the above reaction is catalysed. It is, therefore, stored in wax-lined glass or plastic vessels in dark. Urea can be added as a stabiliser. It is kept away from dust because dust can induce explosive decomposition of the compound.