GROUP 18 ELEMENTS - NOBLE GASES
Group 18 elements: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe) and radon (Rn) having the electronic configurationns2np6,are named as noble gases. All these are gases and chemically unreactive.
Occurrence of group 18 elements
All these gases except radon and oganesson occur in the atmosphere. Their atmospheric abundance in dry air is ~ 1% by volume of which argon is the major constituent. Helium and sometimes neon are found in minerals of radioactive origin e.g., pitchblende, monazite, cleveite. The main commercial source of helium is natural gas. Xenon and radon are the rarest elements of the group. Radon is obtained as a decay product of226Ra.
![]()
Oganesson has been synthetically produced by collision of ![]() atoms and
atoms and ![]() ions
ions
![]()
The elements present in Group 18 have their valence shell orbitals completely filled and, therefore, react with a few elements only under certain conditions. Therefore, they are now known as noble gases.
Oganesson has its symbol Og, atomic number 118, atomic mass 294 and electronic configuration [Rn] 5f146d107s27p6. Only very small amount of Og has been produced. Its half life is 0.7 milliseconds. Therefore, mainly predictions about its chemistry have been made.
Electronic Configuration of group 18 elements
All noble gases have general electronic configurationns2np6except helium which has 1s2. Many of the properties of noble gases including their inactive nature are ascribed to their closed shell structures.
Atomic and Ionic Radii of group 18 elements
Atomic radii of noble gases increases down the group due to the addition of a new shell at each step.
He < Ne < Ar < Kr < Xe < Rn
Ionisation enthalpy of group 18 elements
They have very high ionization enthalpy because of completely filled orbitals. Ionisation enthalpy decreases down the group because of increase in size.
He < Ne < Ar < Kr < Xe < Rn
electron gain enthalpy of group 18 elements
Because of stable electronic configuration, noble gases have no tendency to accept the electron and therefore, have large positive values of electron gain enthalpy.
Physical Properties of group 18 elements
All the noble gases are monoatomic. They are colourless, odourless and tasteless. They are sparingly soluble in water. They have very low melting and boiling points because the only type of interatomic interaction in these elements is weak dispersion forces. Helium has the lowest boiling point (4.2 K) of any known substance. It has an unusual property of diffusing through most commonly used laboratory materials such as rubber, glass or plastics.
Chemical Properties of group 18 elements
Xenon-fluorine compounds
Xenon forms three binary fluorides, XeF2, XeF4and XeF6.
Preparation:

Properties:
XeF2is linear, XeF4is square planar and XeF6is distorted octahedral.
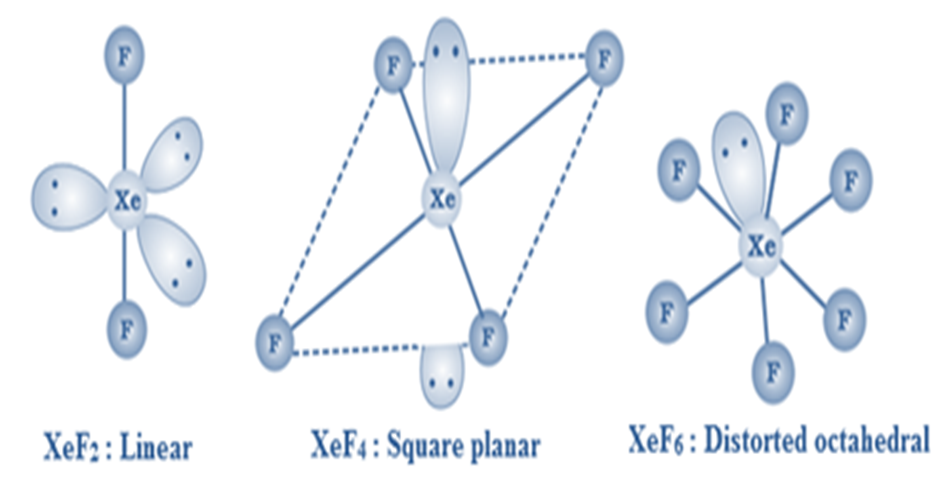
XeF2, XeF4and XeF6are colourless crystalline solids
They are readily hydrolysed
2XeF2(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2Xe(g) + HF(aq) + O2(g)
They react with fluoride ion acceptors to form cationic species and fluoride ion donors to form fluoroanions.
XeF2+ PF5→ [XeF] + [PF6]─
XeF4+ SbF5→ [XeF3]+[SbF6]─
XeF6+ MF → M+[XeF7]─
[Where, M = Na, K, Rb or Cs]
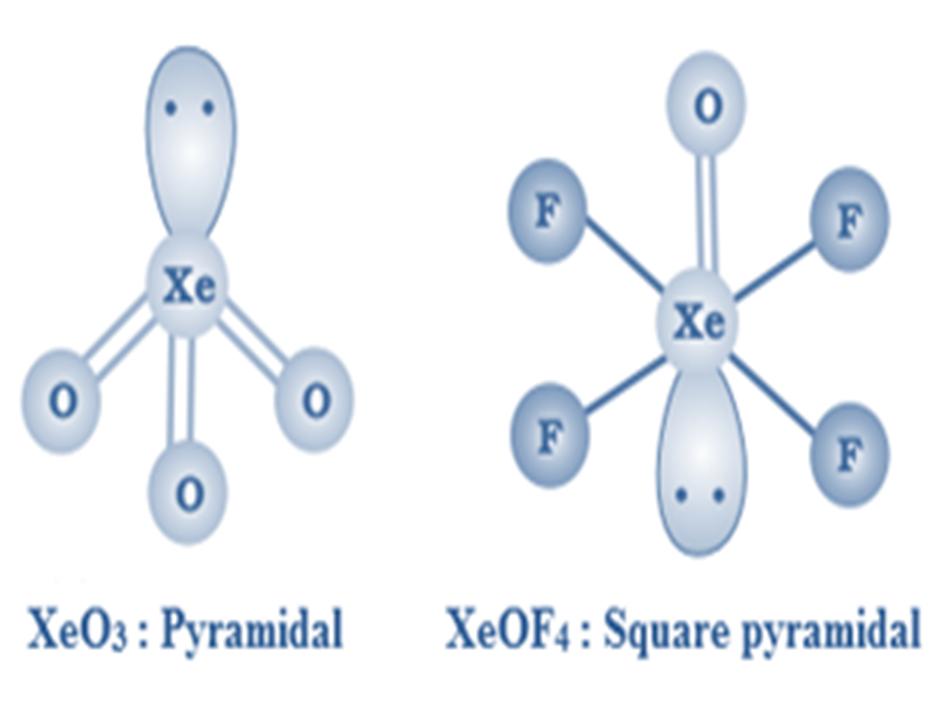
Xenon forms some important compounds with oxygen like XeO3, XeOF4XeO2F2.
Preparation:
Various xenon-oxygen compounds are prepared as follows:
6XeF4+ 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3+ 24HF + 3O2
XeF6+ 3H2O → XeO3+ 6HF
Partial Hydrolysis XeOF4
XeF6+ H2O → XeOF4+ 2 HF
Partial Hydrolysis also gives XeO2F4
XeF6+ 2H2O → XeO2F4+ 4HF
Properties:
XeO3is a colourless explosive solid having a trigonal pyramidal structure.
XeOF4is a colourless volatile liquid with a square pyramidal
Uses of inert gases
Helium is used:
• Gas cooled Nuclear reactors
• In filling balloons for meteorological observations.
• In the oxygen mixture of deep sea divers
• In inflating aeroplane tyres
• Used to provide an inert atmosphere in melting and welding of easily oxidizable metals.
Neon is used:
• In discharge tubes and fluorescent bulbs used for advertising purposes
• In beacon lights for the safety of air navigators as the light can easily pass through the fog for a clear view.
Argon is used:
• To provide an inert atmosphere in high-temperature metallurgical processes (arc welding of metals or alloys)
• For filling electric bulbs.
• In the laboratory for handling substances that are air-sensitive.
• Xenon and Krypton are also used in light bulbs.