A system of two equal and opposite charges separated by a certain distance is called an electric dipole.
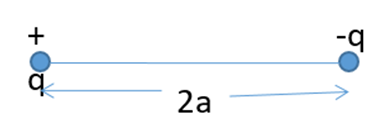
Figure represents an electric dipole consisting of two charge – q and + q and separated by distance 2a. This distance is called length of the dipole and is a vector
It is denoted by vector
Unit of Dipole moment is coulomb metre (C m).
The electric field
Now, q (2a) = p, the magnitude of the electric dipole moment of the dipole.
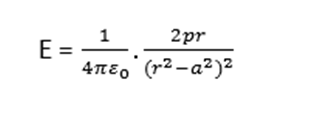
It may be noted that direction of electric field at a point on axial line of the dipole is from charge –q to +q i.e. same as that of electric dipole moment of the dipole. Therefore, in vector notation,
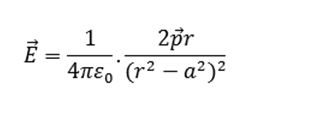
When dipole is of very small length
If the dipole is of small length, such that a2 can be neglected as compared to r2. Therefore, for an electric dipole of very small length
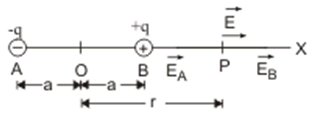
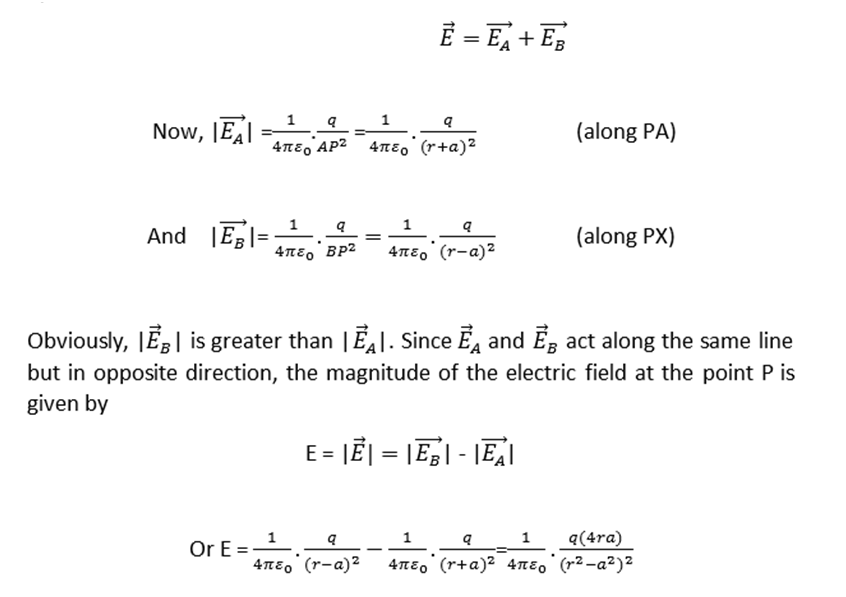
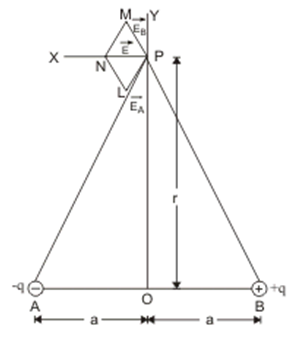
Electric field on equatorial line of an electric dipole
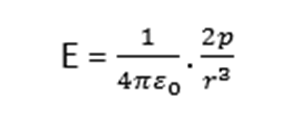
Consider an electric dipole consisting of charges –q and +q separated by a distance 2a and placed in free space. Let P be a point on equatorial line of the dipole (right bisector of the length of dipole) at a distance r from the centre of the dipole.
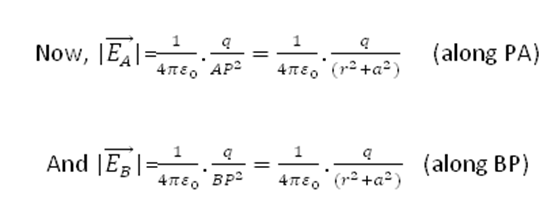
Let
It may be noted that direction of electric field at a point on the equatorial line of the dipole is from charge +q to –q i.e. opposite to the direction of electric dipole moment of the dipole. Therefore, in vector notation,
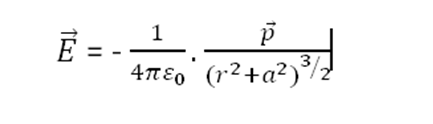
When dipole is of very small length
If the dipole is of small length, such that a2 can be neglected as compared to r2. Therefore, for an electric dipole of very small length,
E =
Torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field
Consider an electric dipole consisting of charges – q and +q and of length 2a placed in a uniform electric field
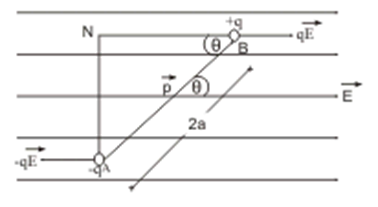
Force on charge – q at A = - q
And force on charge + q at B = q
Thus, electric dipole is under the action of two equal and unlike parallel forces, which gives rise to a torque on the dipole. The magnitude of the torque is given by
= q E (AN) = q E (2 a sin θ) = q (2a) E sin θ
Or
Here, p = q (2a) is electric dipole moment of the electric dipole
The torque on the dipole tends to align it along the direction of the electric field.
Since electric dipole moment vector
1. It may be pointed out that when dipole is placed in uniform electric field, it experiences only a torque. Net force on the dipole is zero.
2. Torque on the dipole becomes zero, when it aligns itself parallel to the electric field.
3. Torque on the dipole is maximum, when dipole is placed at right angles to the direction of the electric field.