Cnidaria:
- Also known as coelenterata.
- They are aquatic, mostly marine, sessile or free-swimming.
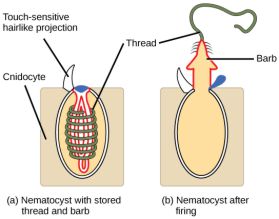
- The name is derived from the cnidoblasts or cnidocytes (which contain the stinging capsules or nematocysts) present on the tentacles and the body.
- Corals have a skeleton composed of calcium carbonate.
- Digestion is extracellular and intracellular.
Characteristics-
- Body Organization:
- Cnidarians exhibit radial symmetry, meaning their bodies are arranged around a central axis, allowing multiple planes of symmetry and are diploblastic.
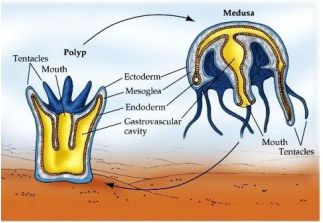
- They have two basic body forms: polyps and medusae.
- Polyps are cylindrical and typically sessile.
- Medusae are umbrella-shaped and free-swimming.
- Cnidarians have specialised cells called cnidocytes, which contain stinging structures called nematocysts used for prey capture and defence.
- Locomotion:
- Many cnidarians, such as jellyfish, exhibit a pulsating movement by contracting and relaxing their bell-shaped medusa body form, allowing them to swim in the water.
- Polyps are generally immobile and use their tentacles to capture prey.
- Reproduction:
- Cnidarians can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
- Asexual reproduction occurs through budding, where new individuals develop as outgrowths from the parent organism.
- Sexual reproduction involves the production of eggs and sperm. Cnidarians can have separate sexes (male and female) or be hermaphroditic.
- Fertilisation may occur internally or externally, depending on the species. The resulting zygote develops into a larval form called a planula, which eventually settles and grows into a polyp.
- Those cnidarians which exist in both forms exhibit alternation of generation called Metagenesis, i.e., polyps produce medusae asexually and medusae form the polyps sexually (e.g. Obelia).
- Feeding Strategies:
- Cnidarians are carnivorous and use their specialised tentacles armed with stinging cells (cnidocytes) to capture prey.
- They typically feed on small organisms, such as plankton and small fish.
- Once prey is captured, cnidarians use their tentacles to immobilise and bring the prey into their mouth, which leads to a central digestive cavity called the gastrovascular cavity. The prey is then digested, and nutrients are distributed throughout the body.
- Examples:
Aurelia (Medusa), Adamsia is a Polyp (Sea anemone) , Physalia (Portuguese man-of-war), Pennatula (Sea-pen), Gorgonia (Sea-fan) and Meandrina (Brain coral).
Ctenophora
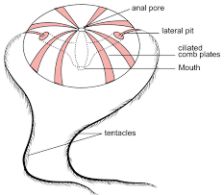
- Commonly known as sea walnuts or comb jellies.
- They are marine.
- Shows bioluminescence (the property of a living organism to emit light).
- Digestion is both extracellular and intracellular.
Characteristics-
- Body Organization:
- They have a gelatinous, transparent body with a radial symmetry, diploblastic with tissue level or organisation.
- They have eight comb-like rows of cilia, called ctenes, which they use for locomotion.
- Locomotion:
- Ctenophores use their cilia to move through the water in a coordinated, swimming motion.
- By beating their cilia in a synchronised pattern, they create water currents that propel them forward.
- Reproduction:
- Ctenophores have separate sexes (male and female).
- They reproduce sexually, with males releasing sperm into the water, which is then captured by females. Fertilisation occurs externally.
- After fertilisation, ctenophores develop into a larval form known as a cydippid, which eventually transforms into the adult body form.
- Feeding Strategies:
- Ctenophores are also carnivorous, feeding primarily on small planktonic organisms.
- They possess specialised sticky cells called colloblasts, located on their tentacles, which they use to capture prey.
- Once prey is captured, ctenophores bring it into their mouth, where it enters a gastrovascular cavity for digestion. Waste is expelled through the same opening.
- Examples:
Pleurobrachia and Ctenoplana.