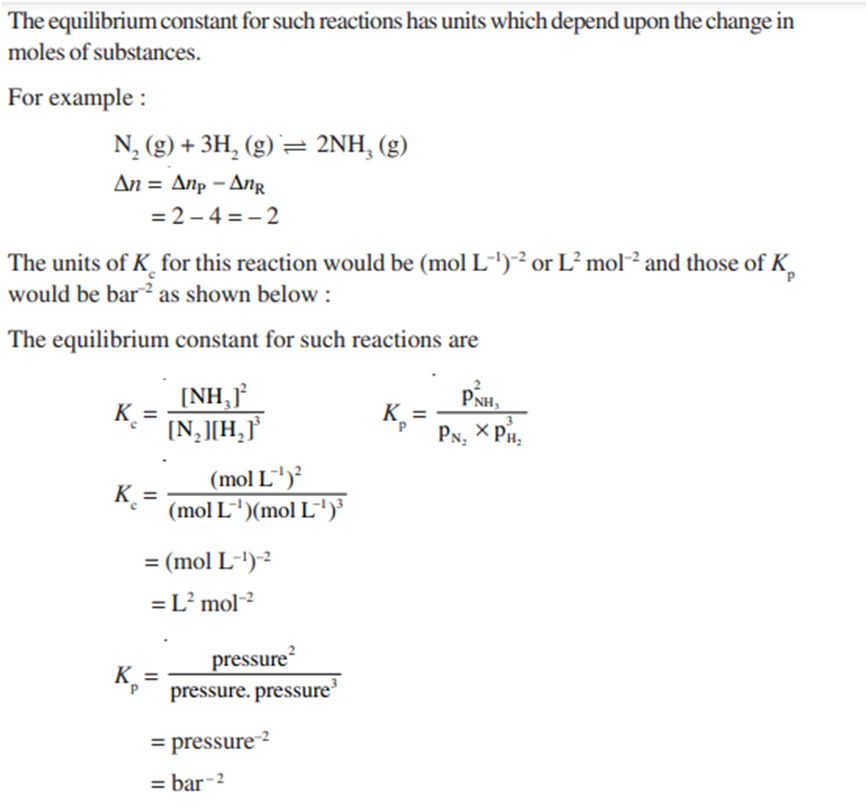Homogeneous equilibrium
In a homogeneous system, all the reactants and products are in the same phase. For example, in the gaseous reaction,
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ![]() 2NH3(g), reactants and products are in the homogeneous phase. Similarly, for the reactions,
2NH3(g), reactants and products are in the homogeneous phase. Similarly, for the reactions,
CH3COOC2H5(aq) + H2O (l) ![]() CH3COOH (aq) + C2H5OH (aq)
CH3COOH (aq) + C2H5OH (aq)
and, Fe3+(aq) + SCN–(aq) ![]() Fe(SCN)2+(aq)
Fe(SCN)2+(aq)
all the reactants and products are in homogeneous solution phase.
Equilibrium Constant in Gaseous Systems
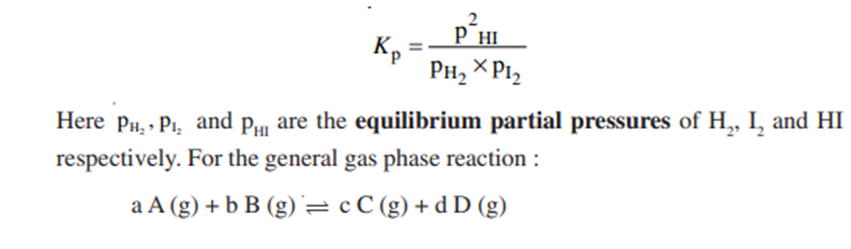

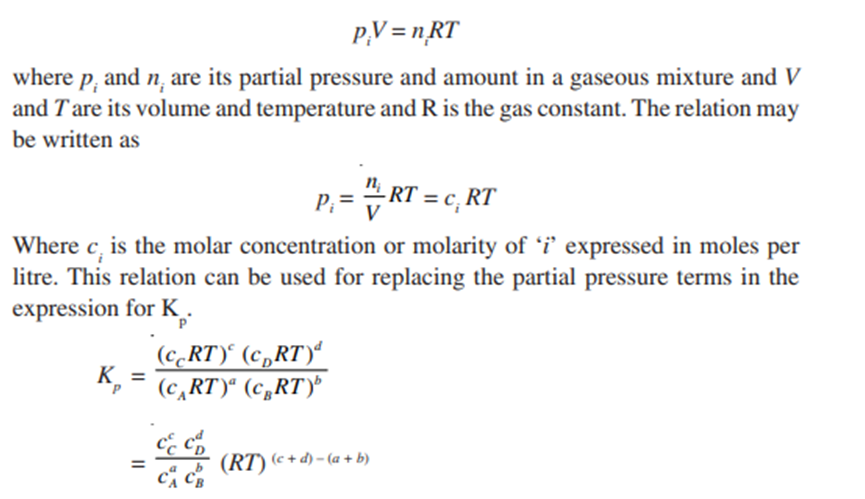
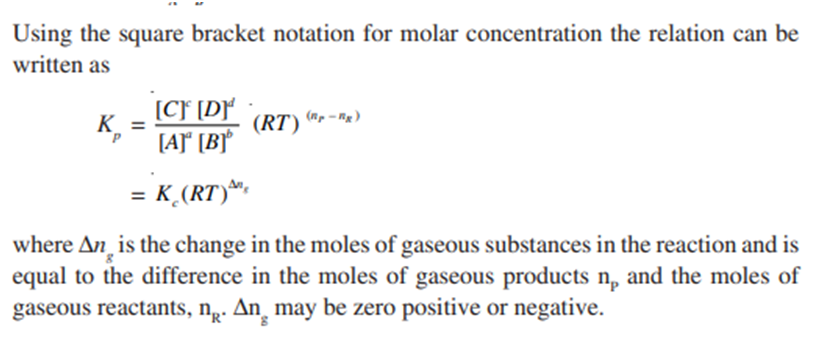
Relation between Kp and Kc
For a general gas phase reaction at equilibrium
![]()
The pressure and concentration equilibrium constants Kp and Kc are
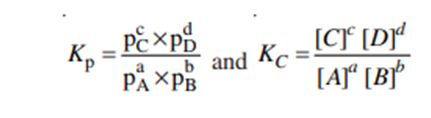
For a gaseous substance i, the ideal gas equation is

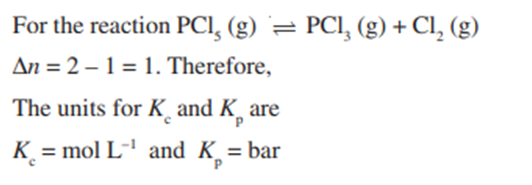
Units of Equilibrium Constant
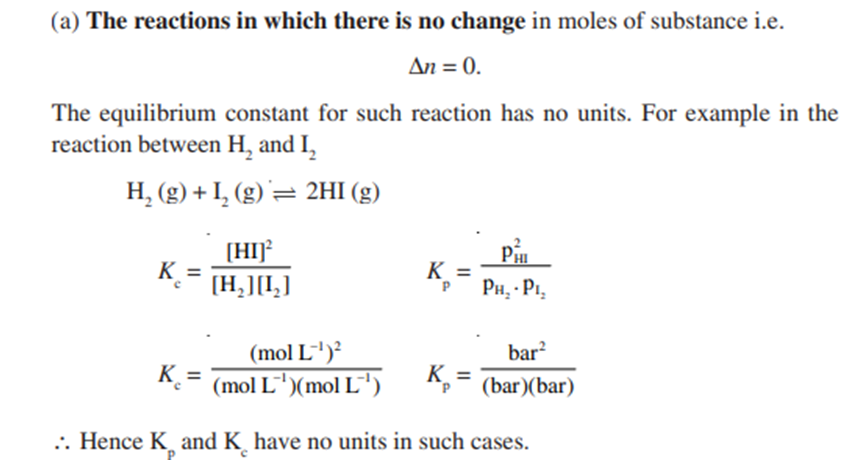
(b) The reaction where there is change in the moles of substance i.e.Δn ≠ 0.