Birth in humans (Parturition):
- Human pregnancy lasts about 9 months, known as the gestation period.
- Parturition is the process of childbirth, induced by a complex neuroendocrine mechanism.
- Signals for parturition come from the fully developed foetus and the placenta, leading to mild uterine contractions called the foetal ejection reflex.
- Foetal ejection reflex triggers the release of oxytocin from the maternal pituitary gland.
- Oxytocin acts on the uterine muscle, causing stronger contractions and further secretion of oxytocin.
- This reflex loop leads to increasingly stronger contractions, resulting in the expulsion of the baby through the birth canal.
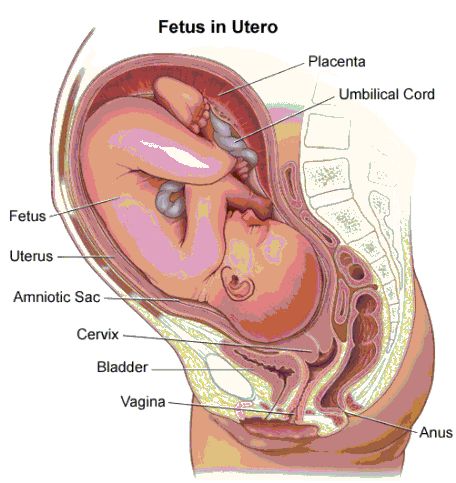
Human foetus inside the uterus
- Induction of Delivery:
- Doctors may use synthetic oxytocin (Pitocin) to induce delivery in certain situations.
- Pitocin is administered intravenously to stimulate uterine contractions and initiate labour.
- Lactation:
- During pregnancy, mammary glands undergo differentiation and preparation for milk production.
- Lactation starts towards the end of pregnancy.
- Milk production is initiated by the process called lactogenesis.
- Colostrum is the milk produced in the initial days after childbirth, rich in antibodies for newborn immunity.
- Breastfeeding during this period is recommended for the baby's health and immunity development.